관련글
Dynamic Programming 관련 포스팅은 여기를 참조
LIS 관련 포스팅은 여기를 참조
유사한 문제인 11053번(가장 긴 증가하는 부분 수열) 포스팅은 여기를 참조
1. 개요
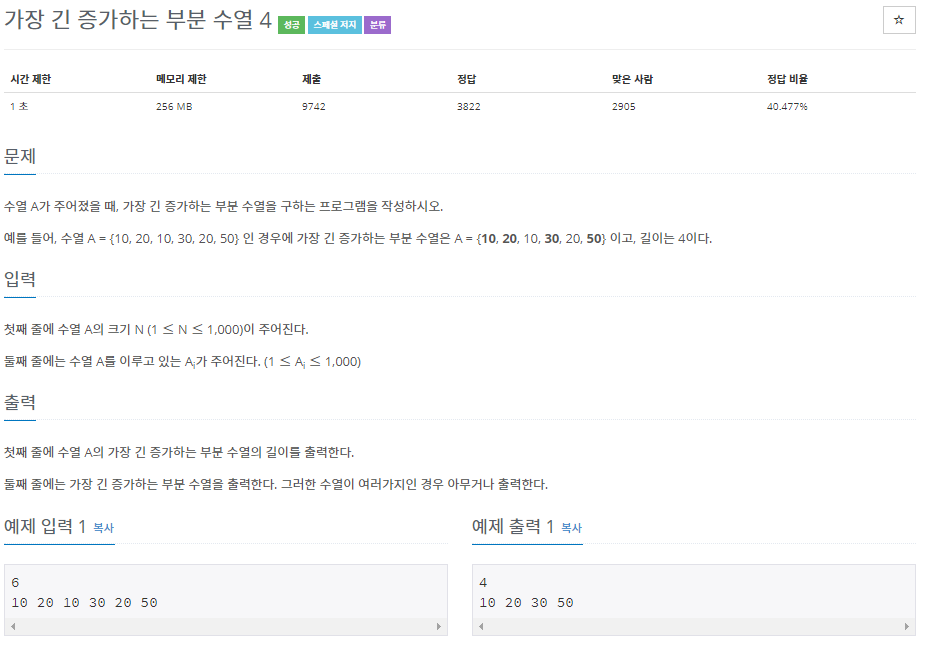
문제 링크는 여기를 참조
문제의 내용을 보려면 아래 더보기 클릭
이 문제는 LIS의 길이 및 그 배열을 구하는 문제이다.
2. 풀이
이 문제는 이전 포스팅의 11053문제와 같은데 추가적으로 LIS의 배열 그 자체까지 출력하는 문제이다. 상단의 관련글 중 링크를 참조하자.
DP문제이므로 간단히 문제의 정의, 기저 상태, 점화식을 알아보자.
정의 : 길이 N의 배열에서 LIS의 길이 및 배열 구하기
길이 N이라는 값 자체가 State이므로 배열의 길이에 따른 결과값만 저장하는 배열을 별도로 생성한다. DP의 결과를 저장할 배열을 lis[]라고 부르자. 그 크기는 기존 배열과 같게 생성하면 될 것이다.
또한 별도로 DP의 결과에 따른 이전 값의 Index를 저장하는 LIS 배열을 V[] 라고 부르자.
그렇다면, 기저 상태는 어떻게 되나? 배열의 길이가 1일 때이다. 즉 N=1, index로는 0일 때, 그 자체로만 LIS가 되므로 그 상태 지정을 할 수 있다. 또한 V배열은 -1로 초기화하여 더 이상 이전 index로 돌아갈 수 없도록 설정한다.
기저 상태 : lis[0] = 1, V[0] = -1
제일 중요한 점화식을 알아보자. LIS의 특성에 따라 점화식은 다음과 같이 지정할 수 있다.
점화식 : lis[i] = lis[j] + 1 (단, j < i and arr[j] < arr[i])
3. 코드
아래의 코드를 통해 정답을 알아보자. 이 방식은 O(nlogn) 방식으로는 풀 수 없다.
1) Bottom-up 방식
import java.io.*;
public class Main{
static int[] arr;
static int[] lis;
static int[] V;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
arr = new int[N];
String line[] = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int i=0; i < N; i++){
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(line[i]);
}
int result = bottomUp(N);
bw.write(String.valueOf(lis[result]) + "\n");
printLis(result, bw);
br.close();
bw.flush();
}
// Bottom-up 방식
public static int bottomUp(int n){
lis = new int[n];
V = new int[n];
// 최대 lis 길이 값
int max_lis = 1;
// 최대 길이를 만족시키는 부분 수열의 마지막 인덱스, 초기는 0으로
int last = 0;
// 반복문을 통해 점화식을 구성하여 최소값을 채워나감
for(int i=0; i < n; i++){
lis[i] = 1; // 각 위치를 1로 우선 초기화
V[i] = -1; // 이전 Index가 돌아갈 곳이 없도록 초기에는 -1로 초기화
for(int j=i-1; j >= 0; j--){
// 이전 값이 더 작으면서 lis 길이 값은 같거나 큰 경우
if(arr[i] > arr[j] && lis[j] >= lis[i]){
lis[i] = lis[j]+1;
V[i] = j; // 이전의 Index를 저장함
}
// 현재 LIS값이 변경된 값보다 작은 경우
if(max_lis < lis[i]){
max_lis = lis[i];
last = i; // 최대 길이가 변경되어야 한다.
}
}
}
return last;
}
// 재귀를 통해 LIS 배열 출력
private static void printLis(int idx, BufferedWriter bw) throws IOException{
// 더 갈 수 없는 가장 이전 index 까지 간 경우
if(V[idx] == -1) {
bw.write(arr[idx] + " ");
return;
}
printLis(V[idx], bw);
bw.write(arr[idx] + " ");
}
}
2) Top-Down 방식
import java.io.*;
public class Main{
static int[] arr;
static int[] lis;
static int[] V;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
arr = new int[N];
lis = new int[N]; lis[0] = 1;
V = new int[N]; V[0] = -1;
String line[] = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int i=0; i < N; i++){
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(line[i]);
}
int result = 0;
for(int i=0; i < lis.length; i++){
int temp = topDown(i);
if(lis[result] < lis[temp]){
result = temp;
}
}
bw.write(String.valueOf(lis[result]) + "\n");
printLis(result, bw);
br.close();
bw.flush();
}
// Top-Down 방식으로 해결하는 DP
public static int topDown(int n){
if(n == 0 || lis[n] > 0) return n; // 기저상태 또는 이미 이전의 값이 있는 경우
lis[n] = 1; // 우선 1로 초기화
V[n] = -1; // V 배열도 -1로 초기화
// 자신보다 이전의 값들과 비교해야함. 그 중 가장 큰 값으로!
for(int i=n-1; i >= 0; i--){
// 우선 먼저 -1로 초기화 시켜둔다.
int temp = -1;
if(arr[i] < arr[n]){
temp = topDown(i);
}
// 만약 -1보다 크게 바뀌었고, lis 길이도 더 긴 경우라면
if(temp != -1 && lis[temp] >= lis[n]){
lis[n] = lis[temp] + 1;
V[n] = temp;
}
}
return n;
}
// 재귀를 통해 LIS 배열 출력
private static void printLis(int idx, BufferedWriter bw) throws IOException{
// 더 갈 수 없는 가장 이전 index 까지 간 경우
if(V[idx] == -1) {
bw.write(arr[idx] + " ");
return;
}
printLis(V[idx], bw);
bw.write(arr[idx] + " ");
}
}
읽어주셔서 감사합니다. 오류가 있으면 지적해주시면 반영하겠습니다.
'알고리즘 풀이(Problem Solving) > Dynamic Programming' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 알고리즘 풀이 - 백준 1699(제곱수의 합, DP) (0) | 2021.01.12 |
|---|---|
| 알고리즘 풀이 - 백준 1912(연속합, DP) (0) | 2021.01.12 |
| 알고리즘 풀이 - 백준 11053(가장 긴 증가하는 부분 수열, DP) (2) | 2021.01.11 |
| 알고리즘 풀이 - 백준 2193(이친수, DP) (0) | 2021.01.08 |
| 알고리즘 풀이 - 백준 10844(쉬운 계단 수, DP) (0) | 2021.01.08 |